Create a map to compare species geographic range and Area of Habitat data. Note that this function requires the ggplot2 package to be installed.
Usage
plot_spp_aoh_data(
x,
max_plot = 9,
expand = 0.05,
zoom = NULL,
maptype = NULL,
maxcell = 50000,
...
)Arguments
- x
sf::st_sf()Object containing the species data. This object should be produced using thecreate_spp_aoh_data()function.- max_plot
integerMaximum number of Area of Habitat datasets to plot. Defaults to 9.- expand
numericProportion to expand the plotting limits. Defaults to 0.05 such that plot limits are extended 5% beyond the spatial extent of the data.- zoom
numericValue indicating the zoom level for the basemap. See documentation for thezoomparameter in theggmap::get_stadiamap()function for details. Defaults toNULLsuch that no basemap is shown.- maptype
characterValue indicating the name of the the basemap to use for the plot. See documentation for themaptypeparameter in theggmap::get_stadiamap()function for details. Defaults toNULLsuch that no basemap is shown. Note that the ggmap package must be installed to show a basemap.- maxcell
integerMaximum number of grid cells for mapping. Defaults to 50000.- ...
Additional arguments passed to
ggmap::get_stadiamap().
Value
A ggplot2::ggplot() object.
Details
Note that data are automatically projected to a geographic coordinate system (EPSG:4326) when they are plotted with a base map. This means that the Area of Habitat data shown in maps that contain a base map might look slightly different from underlying dataset.
Examples
# \dontrun{
# find file path for example range data following IUCN Red List data format
## N.B., the range data were not obtained from the IUCN Red List,
## and were instead based on data from GBIF (https://www.gbif.org/)
path <- system.file("extdata", "EXAMPLE_SPECIES.zip", package = "aoh")
# import data
spp_range_data <- read_spp_range_data(path)
# specify settings for data processing
output_dir <- tempdir() # folder to save AOH data
cache_dir <- rappdirs::user_data_dir("aoh") # persistent storage location
n_threads <- parallel::detectCores() - 1 # speed up analysis
# create cache directory if needed
if (!file.exists(cache_dir)) {
dir.create(cache_dir, showWarnings = FALSE, recursive = TRUE)
}
# create species information data
spp_info_data <- create_spp_info_data(
x = spp_range_data,
cache_dir = cache_dir
)
#> ℹ initializing
#> ✔ initializing [617ms]
#>
#> ℹ cleaning species range data
#> ✔ cleaning species range data [4s]
#>
#> ℹ importing species summary data
#> ✔ importing species summary data [658ms]
#>
#> ℹ importing species habitat data
#> ✔ importing species habitat data [360ms]
#>
#> ℹ collating species data
#> ✔ collating species data [279ms]
#>
#> ℹ post-processing results
#> ✔ post-processing results [16ms]
#>
#> ✔ finished
# create Area of Habitat data for species
spp_aoh_data <- create_spp_aoh_data(
x = spp_info_data,
output_dir = output_dir,
n_threads = n_threads,
cache_dir = cache_dir
)
#> ℹ initializing
#> ✔ initializing [6ms]
#>
#> ℹ importing global elevation data
#> ✔ importing global elevation data [3.9s]
#>
#> ℹ importing global habitat data
#> ! `crosswalk_data` is missing the following 2 habitat classification codes: "7.1", "7.2"
#> ℹ importing global habitat data
#> ✔ importing global habitat data [2.9s]
#>
#> ℹ generating Area of Habitat data
#> skipping 4 species distributions already processed
#> ✔ generating Area of Habitat data [46ms]
#>
#> ℹ post-processing results
#> ✔ post-processing results [16ms]
#>
#> ✔ finished
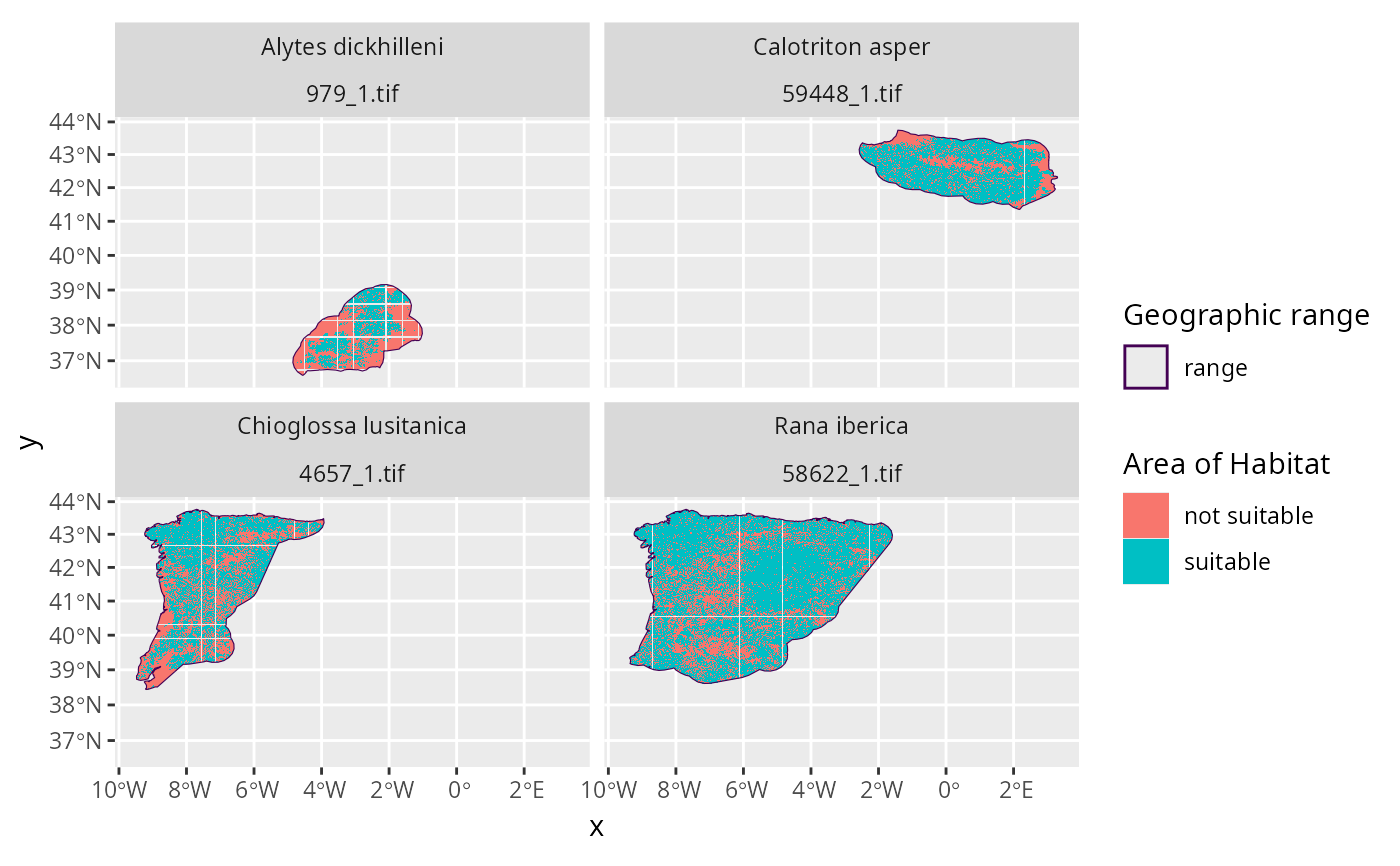
# plot the data to visualize the range maps and AOH data
p <- plot_spp_aoh_data(spp_aoh_data)
print(p)
 # this plot can be customized using ggplot2 functions
# for example, let's style the plot and update the colors
## load ggplot2 package
library(ggplot2)
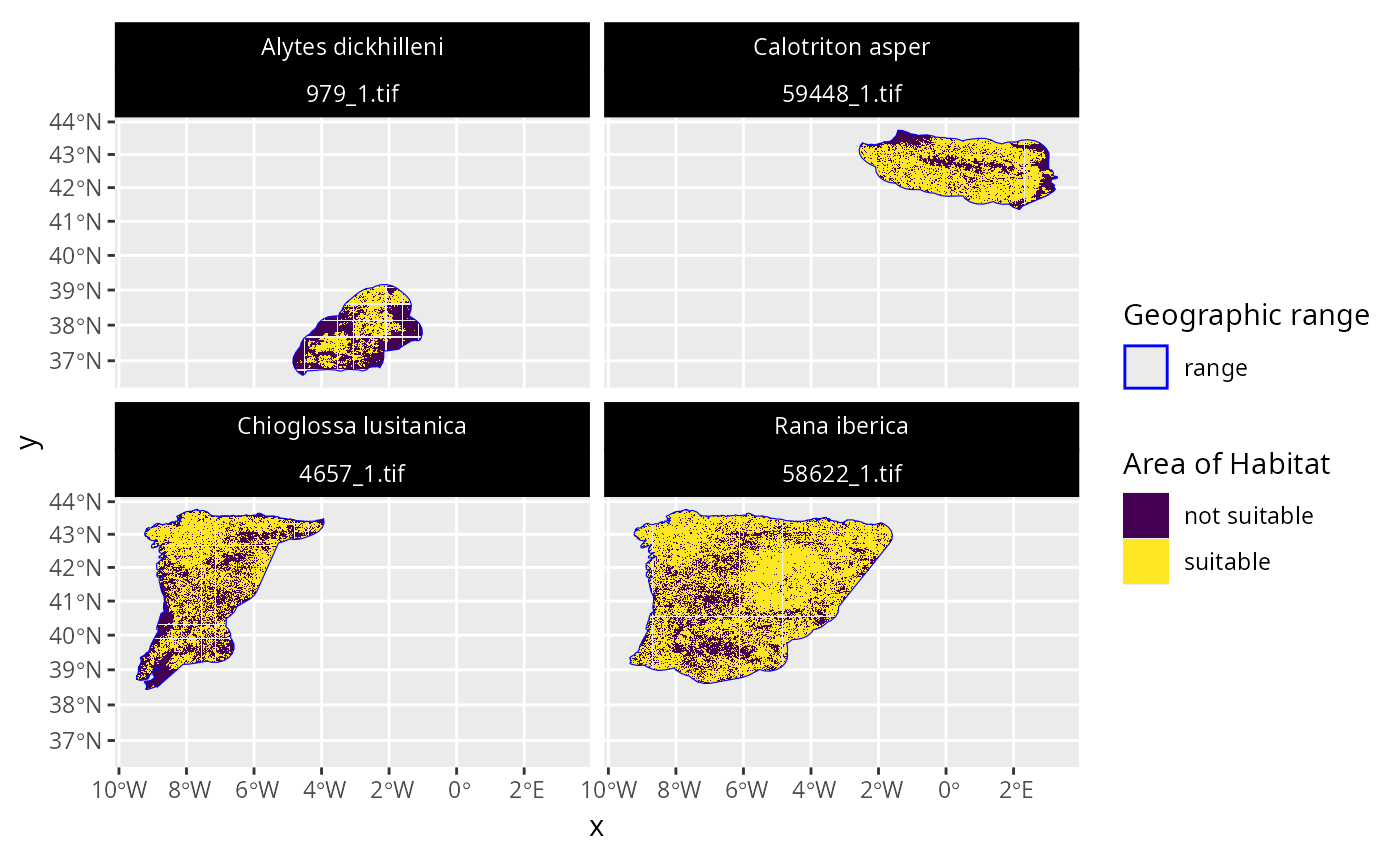
## customize plot
p2 <-
p +
scale_fill_viridis_d() +
scale_color_manual(values = c("range" = "blue")) +
scale_size_manual(values = c("range" = 1.5)) +
theme(
strip.text = ggplot2::element_text(color = "white"),
strip.background = ggplot2::element_rect(
fill = "black", color = "black"
)
)
## print customized plot
print(p2)
# this plot can be customized using ggplot2 functions
# for example, let's style the plot and update the colors
## load ggplot2 package
library(ggplot2)
## customize plot
p2 <-
p +
scale_fill_viridis_d() +
scale_color_manual(values = c("range" = "blue")) +
scale_size_manual(values = c("range" = 1.5)) +
theme(
strip.text = ggplot2::element_text(color = "white"),
strip.background = ggplot2::element_rect(
fill = "black", color = "black"
)
)
## print customized plot
print(p2)
 # }
# \dontrun{
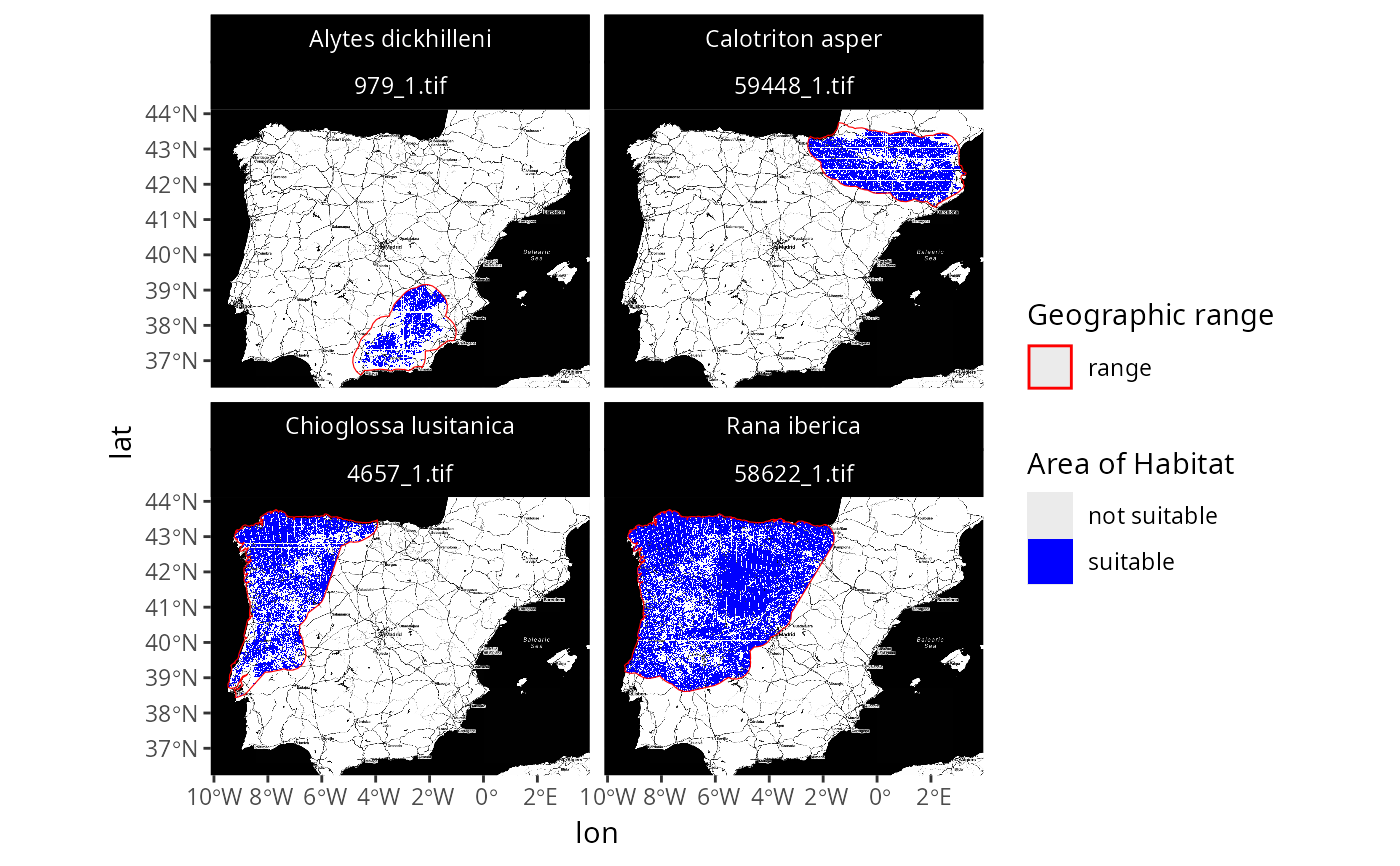
# we can also plot the data with a base map too
## note that you might need to install ggmap to run this example
if (require(ggmap)) {
## create customized map with basemap
p3 <-
plot_spp_aoh_data(spp_aoh_data, zoom = 7, maptype = "stamen_toner") +
scale_fill_manual(
values = c("suitable" = "blue", "not suitable" = "transparent")
) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("range" = "red")) +
scale_size_manual(values = c("range" = 2)) +
theme(
strip.text = ggplot2::element_text(color = "white"),
strip.background = ggplot2::element_rect(
fill = "black", color = "black"
)
)
## print customized plot
print(p3)
}
#> Loading required package: ggmap
#> ℹ Google's Terms of Service: <https://mapsplatform.google.com>
#> Stadia Maps' Terms of Service: <https://stadiamaps.com/terms-of-service>
#> OpenStreetMap's Tile Usage Policy: <https://operations.osmfoundation.org/policies/tiles>
#> ℹ Please cite ggmap if you use it! Use `citation("ggmap")` for details.
#>
#> Attaching package: ‘ggmap’
#> The following object is masked from ‘package:terra’:
#>
#> inset
#> ℹ © Stadia Maps © Stamen Design © OpenMapTiles © OpenStreetMap contributors.
#> Coordinate system already present.
#> ℹ Adding new coordinate system, which will replace the existing one.
# }
# \dontrun{
# we can also plot the data with a base map too
## note that you might need to install ggmap to run this example
if (require(ggmap)) {
## create customized map with basemap
p3 <-
plot_spp_aoh_data(spp_aoh_data, zoom = 7, maptype = "stamen_toner") +
scale_fill_manual(
values = c("suitable" = "blue", "not suitable" = "transparent")
) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("range" = "red")) +
scale_size_manual(values = c("range" = 2)) +
theme(
strip.text = ggplot2::element_text(color = "white"),
strip.background = ggplot2::element_rect(
fill = "black", color = "black"
)
)
## print customized plot
print(p3)
}
#> Loading required package: ggmap
#> ℹ Google's Terms of Service: <https://mapsplatform.google.com>
#> Stadia Maps' Terms of Service: <https://stadiamaps.com/terms-of-service>
#> OpenStreetMap's Tile Usage Policy: <https://operations.osmfoundation.org/policies/tiles>
#> ℹ Please cite ggmap if you use it! Use `citation("ggmap")` for details.
#>
#> Attaching package: ‘ggmap’
#> The following object is masked from ‘package:terra’:
#>
#> inset
#> ℹ © Stadia Maps © Stamen Design © OpenMapTiles © OpenStreetMap contributors.
#> Coordinate system already present.
#> ℹ Adding new coordinate system, which will replace the existing one.
 # }
# }